Rosacea is a chronic skin disorder characterized by redness and visible blood vessels on the face. It usually appears in individuals between the ages of 30 and 50, but it can happen at any age. Although the specific etiology of rosacea is unknown, various factors may contribute to its development. In this article, we'll look at the indications, symptoms, and risk factors associated with rosacea. If you suspect you have rosacea or are suffering from persistent skin problems, you should see a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention and lifestyle changes can aid in the efficient management of rosacea and prevent its progression.
What Is Rosacea and Who Is at Risk?
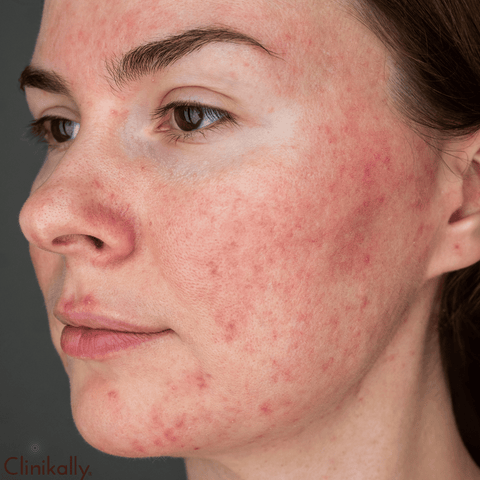
Rosacea is a widespread and chronic skin condition that mostly affects the face, resulting in redness, visible blood vessels, and occasionally acne-like pimples. It most commonly affects adults between the ages of 30 and 50, but it can affect anyone at any age. Rosacea affects both men and women, however, women are more likely to be diagnosed. Rosacea symptoms and indicators vary from person to person, but the most frequent include face redness, visible blood vessels (telangiectasia), acne-like pimples, facial flushing, eye problems, and an enlarged nose (rhinophyma). If you suspect you have rosacea or recurrent skin problems, you should see a dermatologist.
Rosacea: A Chronic Inflammatory Skin Condition
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder affecting mostly the face. It is characterized by episodes of facial redness, visible blood vessels, and the formation of acne-like pimples. If left untreated, the illness is likely to persist and worsen over time. Although rosacea can affect people of various ages, it is most typically diagnosed in adults aged 30 to 50. Rosacea's primary characteristics and symptoms include:
-
Facial Redness: Persistent redness on the central part of the face, particularly the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin. The redness may come and go, but it may become more noticeable over time.
-
Visible Blood Vessels (Telangiectasia): Small, visible blood vessels (spider veins) may appear on the skin's surface due to capillary dilation.
-
Acne-Like Bumps: Some people with rosacea may develop papules and pustules, which are small red bumps and pus-filled lesions. These can be confused with acne, but they are not the same thing.
-
Facial Flushing: Episodes of facial flushing or blushing in which the skin becomes intensely red and may feel warm or hot.
-
Eye Symptoms: Rosacea can affect the eyes in some cases, causing redness, dryness, a gritty sensation, burning, and increased sensitivity to light.
-
Rhinophyma (Enlarged Nose): In rare cases, particularly in untreated or severe rosacea, the skin on the nose may thicken and enlarge, resulting in rhinophyma.
Factors that Increase the Risk of Developing Rosacea
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing rosacea. While the exact cause of rosacea is unknown, the following risk factors may contribute to its development:
-
Genetics: Family history influences the development of rosacea. If you have a close relative who has rosacea, you may be at a higher risk of developing the condition.
-
Fair Skin: People with fair skin, especially those with Celtic or Northern European ancestry, are more likely to experience rosacea. Because there is less melanin, the pigment that naturally protects skin from UV radiation, people with lighter skin tones are more likely to develop rosacea.
-
Age and gender: Although rosacea can affect people of all ages, diagnoses of the condition are most frequently made in adults between the ages of 30 and 50. Women are slightly more likely to develop rosacea, but men can develop more severe forms of the condition, such as rhinophyma.
-
Environmental Factors: A variety of environmental factors can aggravate rosacea symptoms or cause flare-ups. Exposure to sunlight, hot or cold weather, wind, humidity, and sudden temperature changes are all common triggers.
-
Dietary Triggers: Certain foods and beverages have been linked to rosacea flare-ups in some people. Spicy foods, hot beverages, alcohol (particularly red wine), and caffeine are all potential dietary triggers.
-
Emotional Stress: For some people, stress and strong emotions can trigger or worsen rosacea symptoms. Emotional stress, anxiety, and embarrassment have all been linked to flare-ups.
-
Climate and Weather: Living in areas with extreme temperatures, especially hot and humid climates, can increase the risk of developing rosacea or aggravate existing symptoms.
-
Demodex mites: These microscopic mites live on human skin, particularly in the facial area. An overabundance of these mites in some people may be linked to rosacea development or flare-ups.
-
Gastrointestinal Diseases: There is some evidence linking rosacea to certain gastrointestinal diseases, such as Helicobacter pylori infection. More research, however, is required to establish a clear link.
-
Blood Vessel Abnormalities: Some researchers believe that abnormalities in the blood vessels of the face contribute to the development of rosacea.
Age and Gender Patterns in Rosacea
Rosacea has distinct age and gender patterns in its prevalence and manifestation. While it can affect people of all ages, there are some common trends:
-
Age of Onset: Rosacea typically manifests in people over the age of 30. It is less common in younger people, though cases have been reported in teenagers and even children. The risk of developing rosacea increases with age, and it is more common in adults between the ages of 30 and 50.
-
Gender Differences: Rosacea has different gender distributions concerning its severity and specific subtypes:
-
Prevalence: Rosacea is more frequently diagnosed in women than in men, especially in the early stages. Some studies suggest that women have a higher prevalence rate than men.
-
Severe Cases: While women have a higher overall prevalence of rosacea, men are more likely to develop severe forms of the condition, such as rhinophyma, in which the nose becomes enlarged and bulbous due to tissue thickening.
-
Rosacea subtypes: Rosacea can be divided into several subtypes based on their characteristics. The prevalence of these subtypes varies with age and gender:
-
Rosacea Erythematotelangiectatica: This subtype is distinguished by facial redness and visible blood vessels. It is more prevalent in women.
-
Papulopustular Rosacea: This subtype is characterized by acne-like bumps (papules and pustules) on the face as well as facial redness. It affects both men and women equally.
-
Phymatous Rosacea: Skin thickening and expansion of facial features, most notably the nose (rhinophyma), define this subtype. It is more prevalent in men.
-
Ocular Rosacea: This subtype primarily affects the eyes and is associated with vision problems. It affects both men and women, but in some cases, it may go undiagnosed.
Recognizing the Warning Signs of Rosacea
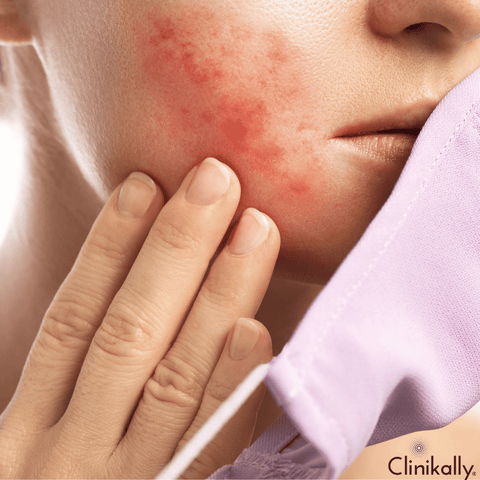
Recognizing rosacea warning symptoms is critical for early diagnosis and efficient treatment of the condition. Rosacea often develops gradually and may be confused for other skin conditions such as acne or sunburn at first. If you notice any of the following warning signs on your face on a regular basis: facial redness, visible blood vessels (telangiectasia), acne-like bumps, facial flushing, eye symptoms, an enlarged nose (rhinophyma), dry, sensitive skin, and triggers, you should see a dermatologist. It's important to note that not everyone with rosacea will exhibit all of these symptoms, and the severity of the symptoms can vary. Furthermore, some symptoms, such as facial redness, might be linked to other disorders, thus, an accurate diagnosis requires careful inspection by a dermatologist. If you suspect you have rosacea or have persistent skin problems, consulting a dermatologist is highly recommended. Early detection and treatment can help control rosacea and improve the overall quality of life for individuals who suffer from it.
Persistent Facial Redness: A Key Indicator of Rosacea
Yes, persistent face redness is a significant symptom of rosacea and one of the disease's most prevalent and distinguishing characteristics. The redness is usually concentrated in the centre of the face, especially on the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin. It may look like a flush or sunburn and come and go, but in rosacea, it is chronic and persistent. This facial redness is typically the first sign of rosacea and is the reason many seek medical assistance. Exposure to sunshine, hot or cold weather, wind, spicy meals, alcohol, caffeine, and emotional stress can all induce or exacerbate it. Rosacea is distinguished by chronic redness caused by dilation of small blood vessels (capillaries) near the skin's surface. These blood vessels continue to have increased blood flow, resulting in evident redness. It is critical to recognize persistent facial redness as a possible rosacea warning sign and seek treatment from a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and management. Early intervention can help control the illness and prevent it from worsening or causing consequences.
Facial Flushing: Temporary Redness and Heat on the Face
Facial flushing is distinguished by a brief reddening of the face, which is frequently accompanied by a sensation of warmth or heat. It is a common physiological response caused by dilated blood vessels near the skin's surface. Because of increased blood flow to the skin as a result of blood vessel dilatation, the skin appears significantly redder and warmer. Emotional triggers, climate fluctuations, spicy meals and drinks, exercise, and certain medical disorders are all causes of face flushing. It is crucial to highlight that face flushing is a natural and usually harmless response in many settings. However, if you experience frequent or persistent facial flushing, especially if it is accompanied by other troubling symptoms, you should seek medical attention.
Visible Blood Vessels: Telangiectasia in Rosacea
Telangiectasia refers to visible blood vessels on the skin in rosacea. Telangiectasia is characterized by the dilatation of small blood vessels (capillaries) near the skin's surface, resulting in the appearance of small, red, or purple spider-like veins. This is a common symptom of rosacea, especially in the erythematotelangiectatic subtype, which is characterized by facial redness and visible blood vessels. In rosacea, telangiectasia most typically develops on the middle area of the face, particularly on the cheeks and nose, but it can also be found on the forehead and chin. The specific etiology of telangiectasia in rosacea is unknown, however, it is thought to be related to the condition's underlying vascular abnormalities and persistent inflammation of the skin. Sun exposure, alcohol consumption, spicy meals, and temperature fluctuations can all cause or aggravate telangiectasia in rosacea patients. Furthermore, genetics and individual skin traits may influence the development of visible blood vessels.
Acne-Like Bumps and Pustules: Rosacea Subtype
Yes, acne-like bumps and pustules are typical of rosacea subtype 2, also known as papulopustular rosacea. This is one of the four types of rosacea, and it is distinguished by persistent facial redness and acne-like breakouts. Individuals with papulopustular rosacea have red papules (small red pimples) and pustules (pus-filled bumps) in the central region of their face, specifically the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin. These pimples can become inflammatory and resemble acne, giving rise to the term "acne rosacea," However, it's crucial to clarify that rosacea is not the same as regular acne.
Papulopustular rosacea's acne-like bumps and pustules can cause discomfort, inflammation, and a negative influence on a person's self-esteem and quality of life. Sun exposure, hot or cold temperatures, spicy foods, alcohol, and stress can all aggravate the symptoms. It is critical to distinguish papulopustular rosacea from typical acne since the treatment techniques are distinct. Standard acne treatments, such as benzoyl peroxide, may not be appropriate for rosacea and may even worsen the condition. Instead, topical or oral antibiotics, topical drugs such as azelaic acid, or other prescription medications to help regulate inflammation and minimize outbreaks may be used to treat papulopustular rosacea.
Eye Symptoms: Ocular Rosacea
Yes, ocular rosacea involves the eyes in rosacea patients. It is a rosacea subtype that affects the eyes and surrounding tissues, resulting in a variety of eye-related symptoms. Ocular rosacea can develop in conjunction with other rosacea subtypes or on its own. Eye redness, dry eyes, burning or stinging sensation, gritty sensations, watery eyes, sensitivity to light, and fuzzy vision are all prominent symptoms of ocular rosacea. As a result, if you suffer any of the above symptoms, especially if you have a history of rosacea or face redness, you should consult an eye care expert or a dermatologist who is knowledgeable about ocular rosacea. Proper diagnosis and care are critical for maintaining eye health and avoiding problems. Artificial tears, lid hygiene, and, in certain situations, prescription drugs to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms may be used to treat ocular rosacea.
Skin Sensitivity: Rosacea and Increased Reactivity
Yes, skin sensitivity and heightened responsiveness are common rosacea symptoms. Rosacea patients frequently have skin that is more sensitive and reactive to different triggers and environmental influences. This increased sensitivity is referred to as "sensitive skin" or "rosacea-prone skin." Facial redness and flushing, burning or stinging sensations, dryness and irritation, sensitivity to topical treatments, increased sensitivity to sunlight, and reactive blood vessels are some of the ways skin sensitivity and enhanced reactivity appear in rosacea. If you have rosacea or suspect you have rosacea-prone skin, consult a dermatologist to build a customized skincare routine and treatment plan. They can assist in identifying triggers, recommending appropriate skincare products, and prescribing drugs to successfully control rosacea and enhance skin comfort.
Skin Thickening: Rosacea Subtype 3 - Phymatous Rosacea
Yes, skin thickening is a hallmark of rosacea subtype 3, often known as phymatous rosacea. This subtype is less common than the others and is characterized by skin thickening on specific parts of the face, most commonly the nose (rhinophyma). However, phymatous rosacea can affect other parts of the face, such as the chin, forehead, cheeks, and ears. The skin swells and becomes bumpy with phymatous rosacea, giving it a bloated and uneven appearance. The expansion of sebaceous (oil) glands and connective tissue in the afflicted areas is chiefly responsible for this thickness. The specific cause of phymatous rosacea is unknown; however, it is thought to be linked to long-term, untreated rosacea, particularly in men. Skin thickening, an enlarged nose (rhinophyma), and a thickened chin, forehead, cheeks, or ears are all symptoms of phymatous rosacea. It's crucial to note that not everyone who has rosacea will develop phymatous rosacea. Phymatous rosacea is more common in people who have severe, long-standing rosacea that has gone untreated for an extended length of time. Although some people are concerned with rhinophyma because of its physical appearance, it is vital to remember that it is a harmless disorder. However, skin thickening might be permanent, causing mental discomfort in those who are affected.
Dry, Rough Skin: Impaired Barrier Function in Rosacea
Yes, dry and rough skin are common symptoms of rosacea and are frequently associated with poor barrier function. The capacity of the skin's barrier function to retain moisture, defend against external influences, and prevent irritants from entering the skin is referred to as its barrier function. This barrier function can be disrupted in rosacea, resulting in a variety of skin issues such as dryness and roughness. Several factors contribute to rosacea's poor barrier function:
-
Chronic Skin Inflammation: Rosacea is linked to chronic skin inflammation. This ongoing inflammatory response may compromise the skin's natural barrier, causing moisture loss and dryness.
-
Altered Moisture Levels: The chronic inflammation in rosacea can affect the skin's ability to retain moisture, resulting in increased transepidermal water loss (TEWL). The skin becomes dry and dehydrated as a result.
-
Reduced Natural Moisturising Factors: The skin contains natural moisturizing factors (NMFs), which aid in water retention and skin hydration. These NMFs may be less present in rosacea, which would increase dryness.
-
Lipid Barrier Disruption: The lipid barrier is a layer of lipids (fats) that aids in keeping moisture in the skin's cells. This lipid barrier may be damaged in rosacea, increasing water evaporation and dryness.
-
Triggers and Irritants: Some triggers, including abrasive skincare products, hot water, or environmental elements like wind and cold weather, can make rosacea patients' skin dry and irritated.
Burning or Stinging Sensation: A Common Complaint in Rosacea
Yes, a burning or stinging feeling is a common complaint among rosacea patients. It is one of the condition's defining symptoms, and it is frequently coupled with facial redness and sensitivity. This sensation can be mild or strong, and it can be triggered or exacerbated by a variety of factors. Rosacea causes a burning or stinging sensation due to a combination of factors such as neurovascular dysregulation, inflammation, triggers, impaired barrier function, and topical irritants. The burning or stinging sensation associated with Rosacea can be distressing, contributing to mental distress and a lower quality of life. As a result, managing this symptom as part of overall rosacea care is critical. If you get a burning or stinging sensation along with other rosacea symptoms, you should consult a dermatologist for examination and treatment. They can give an accurate diagnosis, identify triggers, and recommend appropriate treatment options to help you manage your rosacea and enhance your comfort and well-being.
Swollen or Inflamed Skin: Edema and Inflammation in Rosacea
Yes, rosacea can cause swollen or irritated skin as a result of edema and inflammation. Rosacea is a chronically inflammatory skin condition that primarily affects the face. Inflammation is a major contributor to the development and progression of rosacea, resulting in a variety of skin symptoms and changes. Edoema (fluid buildup), increased blood flow, neurovascular dysregulation, inflammatory mediators, inflammatory papules, and pustules are some of the ways edema and inflammation contribute to swollen or inflamed skin in rosacea. The degree of swelling and inflammation in rosacea can range from mild to severe, and it can change over time depending on various triggers and lifestyle factors. Rosacea skin swollen or inflamed management may include:
-
Identifying and avoiding the causes of inflammation and swelling.
-
Using gentle skincare products designed for sensitive skin to reduce irritation.
-
A dermatologist may prescribe topical or oral medications to reduce inflammation and control rosacea symptoms.
-
Sun protection is important because ultraviolet (UV) radiation can aggravate rosacea.
Identifying Rosacea Triggers and Managing Flare-Ups

Identifying rosacea triggers and managing flare-ups successfully are critical stages in controlling the condition and reducing its overall impact on your everyday life. Triggers are personal variables that might aggravate rosacea symptoms or cause flare-ups. Identifying and avoiding these factors can help to lessen the frequency and severity of rosacea flare-ups. Sun exposure, temperature extremes, spicy meals, hot beverages, alcohol and caffeine, mental stress, skincare products, hot water, wind and humidity, exercise, topical treatments, and a trigger diary are some typical rosacea triggers and management measures. It's crucial to note that triggers differ from person to person; therefore, identifying your individual triggers through observation and the trigger journal is critical. You can effectively control your rosacea and minimize flare-ups by avoiding triggers and working closely with your dermatologist to build a personalized care plan. If your symptoms persist or worsen despite your attempts to limit triggers, talk to your dermatologist about further treatment options and techniques.
Common Triggers: Sun Exposure, Spicy Foods, and more
The most common causes of rosacea flare-ups vary from person to person, but certain factors have been observed to aggravate rosacea symptoms on a regular basis. Sun exposure, spicy meals, hot beverages, alcohol, caffeine, heat and cold exposure, emotional stress, specific skincare products, hard exercise, hormonal changes, and medications are all typical causes of rosacea flare-ups. Remember that triggers might be unique to each person, so pay attention to your particular responses and keep a trigger journal to document potential triggers. You can better control your rosacea and lessen the frequency and severity of flare-ups by identifying and avoiding triggers. If you are unsure about certain triggers or require additional assistance in managing your rosacea, see a dermatologist who can provide personalized advice and treatment options.
Emotional Triggers: Stress and Anxiety's Impact on Rosacea
Stress and anxiety, for example, can have a major impact on rosacea symptoms. Many rosacea patients say that emotional stress and worry can cause flare-ups and worsen current symptoms. The relationship between emotions and rosacea is complex, involving a number of physiological and pharmacological systems. Vascular Response, Inflammation, Immune System Response, Altered Skin Barrier, and Behavioural Factors are some of the ways stress and anxiety can influence rosacea.
Managing Emotional Triggers:
Managing emotional triggers is critical for effective rosacea management. Here are some strategies for reducing stress and anxiety flare-ups:
-
Stress Reduction Techniques: To help manage emotional stress, practice stress reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or tai chi.
-
Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular physical activity can help reduce stress and promote overall well-being.
-
Healthy Lifestyle: To support emotional well-being, eat a balanced diet, get enough sleep, and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
-
Support System: Reach out to friends, family, or support groups to talk about your feelings and experiences.
-
Professional Support: If stress and anxiety become overwhelming, consider seeking support from a mental health professional or counselor.
Strategies for Managing Rosacea Flare-Ups
Managing rosacea flare-ups entails a combination of lifestyle changes, skincare, and medical treatments to control symptoms and minimize their impact on your daily life. Here are some effective rosacea management strategies:
-
Identify and Avoid Triggers: Keep a trigger diary to identify factors that trigger or worsen your rosacea symptoms. Once you have identified your triggers, make a concerted effort to avoid or reduce your exposure to them.
-
Sun Protection: Sun exposure is a common cause of rosacea flare-ups. Wear high-SPF sunscreen, seek shade during peak sun hours, and wear wide-brimmed hats and protective clothing to protect your skin.
-
Use Gentle Skincare Products: For sensitive skin, use gentle, fragrance-free, and non-irritating skincare products. Products containing alcohol, astringents, and other potential irritants should be avoided.
-
Keep Your Skin Clean and Hydrated: Use a gentle, non-abrasive cleanser to cleanse your face, and moisturize regularly to help maintain your skin's natural barrier function and prevent dryness.
-
Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Avoid extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, because they can cause skin irritation and flushing.
-
Manage Stress and Anxiety: To manage emotional stress, which can trigger rosacea flare-ups, use stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga.
-
Topical Medications: Work with your dermatologist to develop a tailored treatment plan that may include topical medications to reduce inflammation and manage rosacea symptoms effectively.
-
Oral Medications: To help control rosacea flare-ups, your dermatologist may prescribe oral medications such as antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs.
-
Laser Therapy: For persistent redness or visible blood vessels, laser therapy may be an option to target and reduce these symptoms.
-
Avoid Excessive Rubbing or Touching Your Face: Excessive rubbing, scratching, or touching your face can aggravate irritation and inflammation.
-
Wear Protective Clothing: In extreme weather conditions, protect your face from wind and cold by wearing a scarf or face mask.
-
Dietary Considerations: While specific trigger foods vary from person to person, it may be beneficial to avoid or limit known trigger foods, such as spicy foods and alcohol.
-
Consistency in Treatment: Adhere to your prescribed treatment plan consistently, even when your symptoms improve, to maintain long-term control over rosacea flare-ups.
-
Regular Follow-ups: Schedule regular follow-up visits with your dermatologist to monitor your progress and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Seeking Professional Help: Diagnosis and Treatment Options

If you suspect you have rosacea or are having symptoms consistent with the illness, consult a dermatologist immediately. A dermatologist is a medical practitioner who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of skin disorders such as rosacea. A dermatologist visit will include a medical history, physical examination, symptom evaluation, skin type and condition, differential diagnosis, and discussion of triggers. Based on the findings, your dermatologist will make a definitive diagnosis and propose a treatment strategy. Topical drugs, oral medications, laser or light therapy, moisturizers and skincare, trigger management, and follow-up visits are among the treatment options for rosacea. It is critical to be proactive in obtaining professional aid since early intervention and good management can result in better rosacea control and a higher quality of life. If you have skin concerns or suspect you have rosacea, make an appointment with a dermatologist for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
Consulting a Dermatologist for Rosacea Evaluation
Consulting a dermatologist for rosacea evaluation is an important step towards obtaining an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. A dermatologist is a medical specialist who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of skin conditions such as rosacea. Here's what to expect during your rosacea evaluation visit to a dermatologist:
-
Medical History: Your dermatologist will begin by taking a detailed medical history, which will include any symptoms you are experiencing, the length of time you have had them, and any factors that appear to trigger or worsen your symptoms.
-
Physical Exam: The dermatologist will examine your skin thoroughly, focusing on areas of redness, flushing, and other symptoms. They may also examine your eyes if you have ocular rosacea.
-
Symptom Assessment: Your dermatologist will ask you detailed questions about your symptoms, such as facial redness, flushing, burning, stinging, dryness, and the presence of bumps or pimples.
-
Triggers: The dermatologist will ask about any potential triggers that may be causing your rosacea symptoms, such as sun exposure, spicy foods, alcohol, stress, or temperature changes.
-
Differential Diagnosis: Because rosacea is similar to other skin conditions, your dermatologist will consider and rule out other possible causes of your symptoms using a process known as differential diagnosis.
-
Skin Type and Condition: Your dermatologist will evaluate your skin type and condition to determine the best treatment plan for you.
-
Medical Tests: The dermatologist may order additional tests to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other conditions in some cases.
Rosacea Treatment Approaches: Medications and Lifestyle Changes
Rosacea treatment usually consists of a mix of drugs and lifestyle adjustments designed to successfully manage symptoms and reduce flare-ups. The specific treatment strategy will differ depending on the degree and subtype of rosacea, as well as personal characteristics. Here are some common rosacea treatment methods:
-
Topical Medications: Prescription topical medications are frequently used as the first-line treatment for mild to moderate rosacea. These might include ivermectin, azelaic acid, and metronidazole.
-
Oral medications: Oral medications may be prescribed in more severe cases or when topical treatments are insufficient. Oral antibiotics and low-dose isotretinoin are common treatments.
-
Laser and light therapy: These treatments target visible blood vessels and rosacea-related redness. They can improve the overall appearance of the skin and reduce flushing. In this case, intense pulsed light (IPL) and vascular lasers are commonly used.
-
Changes in Lifestyle: Certain lifestyle changes can help manage rosacea and prevent flare-ups. Sun protection, dietary changes, stress management, gentle skincare, and temperature control are all examples of lifestyle changes that may be beneficial.
-
Eye Care: If you have ocular rosacea, your dermatologist or an eye care professional may recommend specific treatments to manage eye symptoms, such as artificial tears, lid hygiene, or medications.
The Importance of Early Intervention in Rosacea Management
For numerous reasons, early intervention in rosacea therapy is critical. When rosacea is detected and treated early, it can result in better outcomes, improved symptom control, and a higher quality of life for those suffering from the condition. Early intervention is critical in rosacea therapy for several reasons, including symptom control, preventing advancement, minimizing flare-ups, preventing complications, emotional well-being, avoiding unnecessary discomfort, personalized treatment, and lowering long-term costs. If you suspect you have rosacea or are having symptoms consistent with the condition, it is critical to seek early assessment and treatment from a dermatologist. Individuals with rosacea can effectively control their symptoms, improve their skin health, and improve their quality of life with correct management and timely therapy.