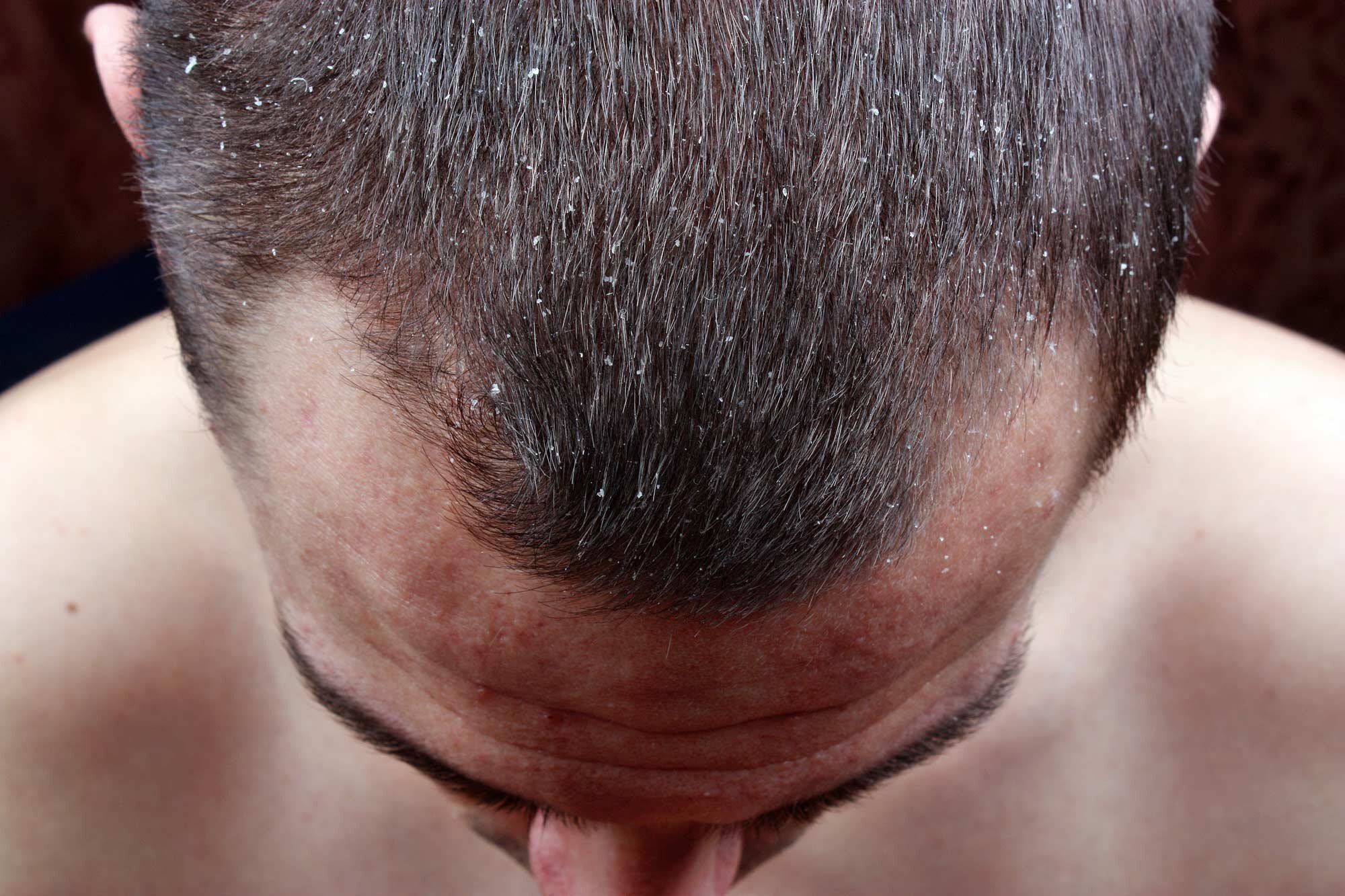
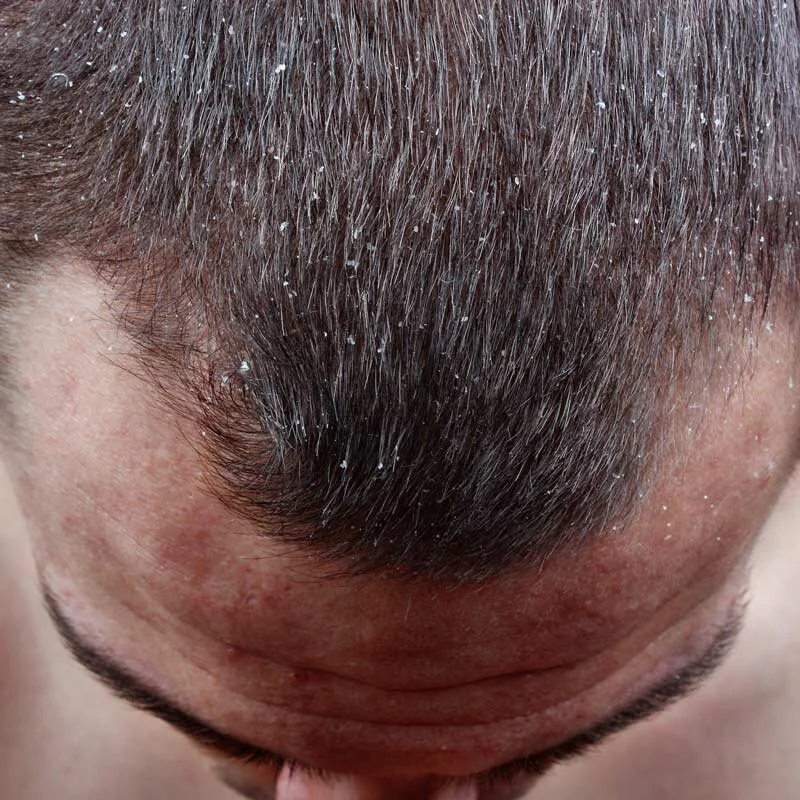
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin condition that is characterized by the presence of red, scaly, and flaky skin on the scalp, face, and other areas of the body. It is a chronic condition that can occur at any age, but it is most commonly found in adults. Seborrheic dermatitis is not contagious and is not caused by poor hygiene.
The exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis is unknown, but it is believed to be related to an overproduction of oil (sebum) in the skin and an overgrowth of a yeast-like fungus called Malassezia. Other factors that may contribute to the development of seborrheic dermatitis include:
Hormonal changes: seborrheic dermatitis is more common in people with conditions that cause hormonal imbalances, such as puberty, pregnancy, and menopause
Medical conditions: seborrheic dermatitis may be more common in people with certain medical conditions, such as Parkinson's disease, HIV/AIDS, and neurological disorders
Stress: stress may contribute to the development or worsening of seborrheic dermatitis
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis may include red, scaly, and flaky skin on the scalp, face, and other areas of the body, as well as dandruff, itching, and a burning sensation. The condition may be accompanied by other symptoms, such as redness, swelling, and crusting of the skin.
Treatment for seborrheic dermatitis may involve the use of over-the-counter or prescription medications, such as shampoos, creams, and ointments, to help manage the symptoms of the condition. In some cases, a healthcare provider may recommend a combination of treatments to help manage the condition.
In addition to treatment, there are several steps you can take to help reduce your risk of developing seborrheic dermatitis:
Avoid using harsh or irritating products on the skin
Use a gentle, unscented shampoo and conditioner to help manage dandruff
Avoid tight hairstyles, such as ponytails or cornrows, which can irritate the scalp
Avoid scratching or picking at the affected areas to help prevent the spread of the condition
Manage stress through relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation
By following these precautions and seeking treatment as needed, you can help to manage seborrheic dermatitis and reduce your risk of developing this type of skin condition. If you are concerned about seborrheic dermatitis or have any other changes in your skin, it is important to see a healthcare provider for evaluation and treatment.